Regardless of the pathogen, the disease has similar symptoms, mechanism of occurrence and treatment tactics. Foot fungus is a common and contagious disease. It is characterized by a high frequency of occurrence in the presence of concomitant conditions and diseases, for example, foci of chronic inflammation, endocrine diseases, decreased immune system and other diseases. As a rule, the disease is chronic in nature with exacerbations in the summer and easing of the process (remission) by the winter.
Signs of mycosis
- Color change
- Inflammation
- Appearance of stains
- Erosion
- Deformation and thickening
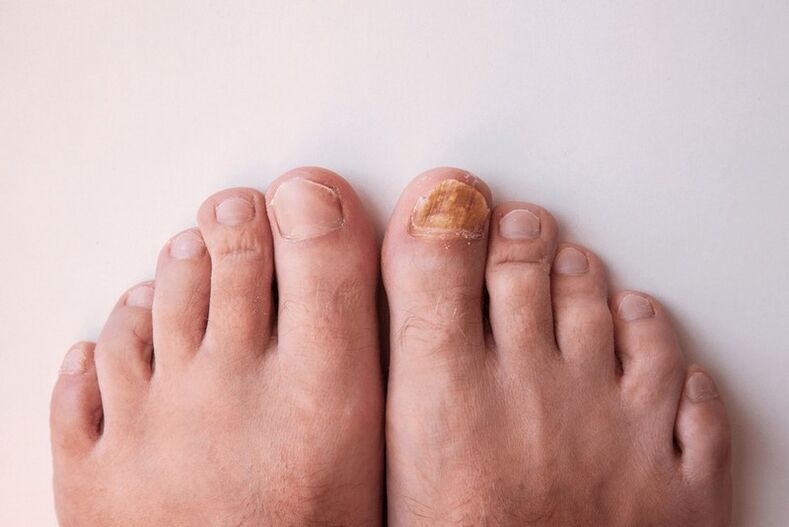
Types of fungal foot diseases
Depending on the types of fungi that cause the disease, foot mycosis are divided into:
Yeast-like mycoses: caused by fungi of the Candida genus.
Mold mycosis: caused by Scytalidium spp. fungi. , Onychocola canadensis, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Aspergillus, Fusarium, Alternaria, Penicillium.
Dermatomycosis: caused by dermatomycetes of the Trichophyton and Epidermophyton genera. Mushrooms of this species require keratin to function, which is rich in the stratum corneum of the skin, nails and hair. The group of dermatomycosis with predominant damage to the nails includes rubrophytosis (the causative agent isTrichophyton rubrum) and athlete's foot (causative agent - Trichophyton interdigitale). Trichophyton rubrum accounts for approximately 80-90% of cases of athlete's foot.
Mixed mycoses: caused by multiple types of fungi at the same time.
Each type of mycosis is described in detail below.
Yeast-like mycoses
Recently, mycosis of the feet caused by fungi of the Candida genus have spread. It is assumed that this is due to the widespread use of various drugs, the action of which is associated with interaction with the immune system.
Dermatomycosis
Athlete's foot is a chronic disease localized on the skin of the arches and interdigital folds of the feet, with frequent damage to the nails.
Mold mycosis
Mold mycosis are especially common in countries where people traditionally walk barefoot (eastern, subtropical and tropical countries). In regions with a temperate climate, this type of mycosis also occurs, but, as a rule, in patients with immunodeficiency conditions and in people who often come into contact with soil and plants.
Forms of mycosis of the feet
There are different forms of mycosis:
Scaly
It is characterized by peeling of the skin on the arches of the feet, which can extend to the surface of the toes. Areas of skin thickening and lamellar scaling may also appear.
Intertriginous
Similar to interdigital diaper rash. The inflammatory process is usually localized between the 3rd and 4th toes. The stratum corneum softens, loosens and flakes. Cracks and a whitish coating appear. Itching and burning begin. The addition of pyococci (pustular infection) and yeast flora is possible, then the affected areas become covered with purulent, bloody crusts.
Dyshidrotic
It is characterized by the appearance on the lateral surface of the feet and on the surfaces of the toes in contact with it, of bubbles filled with a clear liquid and covered by a thick horny layer. Sago grains (vesicles) can be single or coalesce into multichambered bubbles. When pyococci come together, the contents of the vesicles become cloudy, then they open and erosions covered with purulent-hemorrhagic crusts are formed. Some patients note inflammation of the lymph nodes and a deterioration in general health.
Fungi (allergic rash) are observed in 2/3 of patients with intertriginous and dyshidrotic forms of epidermophytosis.
Of course, the identification of clinical forms of epidermophytosis is conditional, since their combination often occurs; one form can transform into another. It all depends on the reaction of the body, physical activity and treatment methods of the patient.
Also, with mycosis of the feet, the nails are often affected, mainly on the first and fifth toes. The nail plate acquires yellowish spots or stripes, the surface becomes dull and uneven, and a horny thickening begins to appear under the nail, which subsequently leads to the destruction of the nail plate.
Looking at the corresponding video on the Internet, you can find that foot fungus can be caused by various factors, and to choose therapeutic tactics for this disease it is necessary to determine the type of fungus and establish the cause of its appearance.
Causes of foot fungus
The main causes of foot fungus are:
- Excessive sweating or, conversely, increased dryness and flaking of the feet. These processes disrupt the protective function of skin cells.
- Anatomical characteristics: narrow spaces between the toes and their deformation, flat feet.
- Problems with thermoregulation (maintenance of a certain body temperature) and microcirculation (transport of biological fluids).
- Wounds, lesions that violate the integrity of the skin. Infections often occur through these lesions.
- The presence of diseases that reduce immunity or lead to metabolic disorders (for example, endocrinopathies, blood diseases, oncology, etc. ).
- Taking some drugs (antibacterials, cytostatics, corticosteroids).
Often fungal infections of the feet are combined with pustular eruptions, so hypotheses are made about the relationship between them: thanks to pyococci, dermatophytes penetrate deep into the subcutaneous tissue and contribute to prolonged mycosis due to the formation of cracks, scratches and erosions. to a greater susceptibility to infections.
Often, with foot fungus, a viral infection occurs. For example, the causative agent of rubromycosis activates papillomaviruses and herpes viruses. This manifests itself in an increased concentration of viruses on the surface of cells infected by fungi.
The source of the spread of the disease is people suffering from mycosis: during the peeling process, skin flakes containing the pathogens of the fungal infection come off. These infected scales often end up on the floor, on swimming pool and bathroom equipment and even on pedicure tools.
An interesting fact is that mushrooms are highly resistant and can be stored in thermal, chlorinated and ozonated waters for 12-18 days. Water with a high salt or hydrogen sulfide content is harmful to mushrooms.
We must therefore remember that the general mechanisms contributing to the development of fungal foot infections are caused by a violation of the body's natural resistance, changes in immune and metabolic processes.
Diagnosis of foot fungus
Diagnosis of foot fungus includes:
- Assess patient complaints and the presence of chronic diseases.
- Microscopic examination of affected skin and nail particles.
- Cultural seeding is the placement of pathogenic microorganisms in a nutrient medium for their reproduction and subsequent accurate identification, as well as to evaluate the activity of antifungal drugs and determine the sensitivity of fungi to them.
To correctly select therapy, it is important to determine whether the changes in the skin of the foot are a fungal infection or dyshidrotic eczema, keratoderma, psoriasis and other skin diseases.
Antifungal drugs, agents, antifungals
Antifungal agents: classification and types of dosage forms. Methods of using antifungals.
Foot fungus treatment
Treatment of foot fungus must be done comprehensively; it is important not only to suppress the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and eliminate symptoms, but also to destroy pathogens and eliminate the cause of their occurrence (increase immunity, immediately treat small wounds on the feet, etc. ). It is imperative to treat concomitant diseases that cause the development of fungal infections.
Additionally, some people may have allergic reactions to certain mushrooms (like mykids). In these cases, antihistamine (antiallergic) drugs may be necessary.
To treat mycoses, topical preparations are usually used, that is, those that are applied directly to the affected area of the skin. Such products are produced in the form of ointments, creams, sprays, solutions and paints (for nails).
Depending on the mechanism of action, antifungal agents can have a fungistatic effect, inhibiting the growth and reproduction of fungi, or they can have a fungicidal effect and promote the death of fungi.
Since foot mycosis is often caused by mixed fungal flora, it is more effective to use broad-spectrum agents. These include drugs that have their own anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects.
The use of special products in the treatment of foot fungus
Modern antifungal drugs are highly effective against pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida, dermatophytes (Trichophyton, Microsporum) and other causative agents of skin infections, gram-positive strains of staphylococci and streptococci. They block the growth and reproduction of fungi (fungistatic effect), destroy fungi (fungicidal effect) when used in therapeutic doses, have their anti-inflammatory and anti-itching effect